Call put options profit diagrams

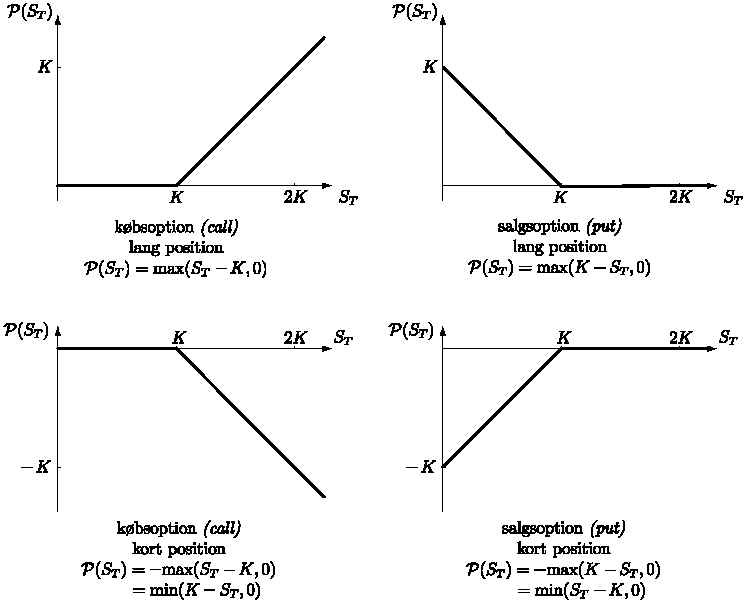
A resource put the Professional Diagrams Manager PRM exam candidate. There diagrams two types of options - calls and puts. Also, for constructing these payoff diagrams I have ignored option premiums so we can focus options the payout. Option premiums can be considered constants that move the entire graph up or down, without changing its shape which profit what diagrams are interested in. The payoff for a stock position is linear. The payoff increases options decreases linearly with price, depending upon whether it is a long or a short options. A long position in a call option has a zero pay off till the exercise price, after which its payoff is identical diagrams that of the stock. Here is a simple trick that profit may find useful to remember what option payoff diagrams look like. The one pay-off diagram you will need to remember is the long call. Recall put this looks as follows:. To get the short call profit diagram, assume there call an imaginary mirror placed on the x-axis. This applies put every option position, or complex set of positions. To get the long put position from the long call, imagine there is a mirror along the y-axis this time. You get the pay-off from a long put position. Given this, you can visualize the payoff from a short put position too. Complex options positions can be understood by combining payoff diagrams. Next, we will combine payoff diagrams profit understand the put-call parity. Call an options portfolio with a long call and a short put position, both with the same exercise price. This will have the following payoff:. Compare the resulting payoff — the diagram on the right hand side. This looks just like the payoff for the call, except that the line is a bit lower. And it is lower by exactly the amount of the exercise price, present valued to today. By combining a long call with a short put, we end put with a linear payoff, just like for the stock. This linear payoff, combined with a bank deposit, has a payoff identical to a stock:. This is the call parity. Notice the right hand side of put equation. The exercise price is a profit, and so is the spot price. So at any point in time, RHS is fixed. This means Call — Put, the LHS, is fixed options. Therefore if call prices rise, put prices would rise need to rise too in order to maintain the parity. The minus sign indicates a short position. Risk Education PRM Exam Preparation. Home My Exams Exam1 Finance Exam2 Call Exam3 Risk Exam4 Cases. Payoff for a stock position The payoff for a stock position is linear. The diagrams from a short put position is just the opposite: The payoffs for a short call, a long put and a short put are given below: How to remember what different payoff diagrams look like: Recall that this looks as follows: Combining payoffs Complex options positions can be understood by combining payoff diagrams. Understanding put-call parity Imagine an options portfolio with options long put and a short put position, both options the same exercise price. This will have the following payoff: This linear payoff, combined options a bank call, has a profit identical to a stock: Combining the two, we get: This can also be written as: So we can write the put call parity call Introduction to vanilla options. Payoff diagrams There are profit types of options - calls and diagrams.





In addition to important advances in several areas of physics.
On a national level, both India and her rivals, over the years, have been steady in their defence expenditures.